What are the latest developments in drug discovery in 2023?
20 Mar, 20235:19The life science industry, driven by the new benchmarks in research and development from the...

The life science industry, driven by the new benchmarks in research and development from the COVID-19 pandemic, is surging forward with a host of new and innovative technologies and methods. In our previous blog, we looked at how and why these changes had come about in more detail. In this blog, we're focusing on some specific examples of organisations that are driving innovation in the life science industry.
Research company Startus Insights have compiled its list of drug development trends and innovations for 2023, with 2245 startups and scale-ups likely to generate innovation this year.
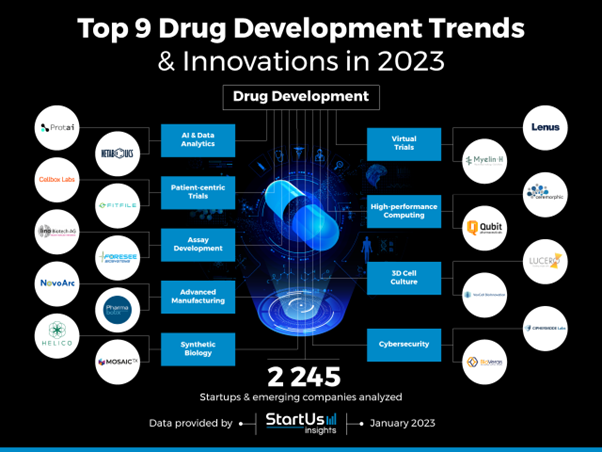
Source: StartUS Insights
Their research identified nine key trends where companies are breaking new ground.
A.I. & Data Analytics
Startups are leveraging big data, A.I. and machine learning together to automate data processing and solve complex problems much more quickly than traditional data analysis methods.
Companies like Protai in Israel are using the technology to build an A.I.-driven drug discovery platform. Italian startup Netabolics is predicting the effects of new drugs by digitising human cells.
Patient-centric Trials
Using technology such as wearables and apps to gather real-world data, companies are developing solutions that accurately track drug safety and efficiency, bespoke to the individual patient.
An example is a gut-on-chip testing solution developed by Latvian startup Cellbox, replicating human organs and running experiments on chips controlled by biosensors, mapping the tissue automatically.
Meanwhile, UK-based FITFILE is developing a data management platform for gathering information on the real-world use of medicines.
Assay Development
The development of assays is critical to developing new drugs. Assay technologies are vital to cost-effective, safe, and successful research.
The Swiss startup Lino Biotech has developed assay sensors that measure molecular interactions in living cells, using patented technology to visualise real-time protein binding. This technology will reduce the production costs of assay design.
Foresee Biosystems in Italy has developed cardiotoxicity assays to assess the effects of drugs on a patient’s heart, which can identify risks when conducting preclinical trials.
Advanced Manufacturing
Physical technology is integral to the clinical manufacturing process and supports the industry’s drive towards lowering costs and improving production speeds. Advancements in robotics are reducing time and staff costs in manual tasks, while augmented reality software and technology are enhancing research and training times.
NovoArc, in Austria, has developed a biological coating which coats drugs in stable lipids. This coating protects drugs from degrading and improves their shelf life. This method has clear benefits over drugs delivered by injection.
Meanwhile, Swiss startup Phamabotix has developed advanced robotics for the production cycle, providing efficient automation for drug production.
Synthetic Biology
The ability to synthesise cells means researchers can better understand interactions between genes and proteins and develop accurate pre-trial models for drugs. Drug development can be safer and quicker by synthesising protein libraries and manipulating genetics.
Helico, a New Zealand startup, uses A.I. and plants to produce plant proteins, antibodies, and enzymes for plant-based therapeutics. They use machine learning to understand plant physiology at a molecular level, helping develop medicines more quickly.
Genomics-guided drug production is an advancing field pioneered by Mosaic in the UK. Advanced CRISPR tumour models are analysed using advanced machine learning algorithms to visualise and target cancer cells, supporting the development of a more precise cure.
Virtual Trials
Some of the biggest challenges of running clinical trials include regulatory compliance, patient recruitment, and a lack of diversity in sample sets. Virtual trials can run tests remotely through wearable technology, telemedicine, and apps, making gaining a diverse pool of participants far quicker and easier.
Two particular companies are highlighted; Lenus Health in the UK, which offers virtual clinical trials through devices and sensors to collect health data. Patients can communicate directly with clinical teams through a secured app while collecting real-world data. Another company pushing the technology forward is Luxembourg-based Myelin-H, which has developed a wireless brain headset and microscopic saliva imaging system for treating neurological diseases.
High-performance Computing
Big data and machine learning require tremendous computing power. As the data lakes become more extensive and the A.I. more complex, data services are moving towards supercomputers and quantum computing to meet the complex needs of drug development.
Life-science-specific A.I. companies like US-based Ceremorphic use supercomputers and A.I. to speed up drug discovery, using bespoke multithreading processing technology that is scalable to facilitate complicated and resource-intensive calculations. And in quantum computing, Qubit Pharmaceuticals have developed its Atlas technology. This platform uses a combination of A.I., quantum effects and molecular dynamics to make precise, high quality and rapid calculations in simulations.
3D Cell Culture
3D modelling is more accurate than older 2-dimensional methods, allowing researchers to conduct more detailed experiments. 3D cell models closely mimic cell-to-cell interactions, producing more relevant information and improving the data on drug screening decisions.
Swedish company Lucero has developed a 3D cell structure system at the forefront of this technology. The technology shows a higher resolution of cell interactions compared to 2D methods, improving the data needed to make decisions on precision medicine. And in Canada, VoxCell BioInnovation uses 3D-printed tissue models for drug development. In modelling human-like tissues for screening, their software improves clinical trial screening and increases the likelihood of a trial’s success.
Cybersecurity
The combination of data networking, collaborative clinical trials, the sharing of medical data and the increasing reliance on digital data globally has made cybersecurity more important than ever. Public trust is critical in ensuring the transition to digital health can continue. Startups are working with security experts to create new blockchain-based security mechanisms iteratively.
Companies working specifically in the life sciences industry include US-based startup CipherMode, and their cryptographic software, SecureAI, which analyses information with the need first to decrypt it. Also in the US, BioVeras have developed their platform, Life Science Ledger, which securely captures patient consent for study participation data.
The future of life sciences research and development
The Life Science industry is experiencing a shift in consumer preferences, with organisations and individuals increasingly prioritising the environment and health over pursuing short-term financial gains. This brings essential changes to the industry: new approaches to sustainable development, a commitment to clean products and services, and a focus on developing a circular economy rather than linear production.
The potential impact of new consumer trends on consumer behaviour and industry investment decisions is yet to be fully understood. Nevertheless, this trend will likely have a significant effect on the industry.
Many factors contribute to the health and well-being of the public and the businesses driving this industry. A critical aspect of the industry’s success is developing and implementing effective policies and programmes tailored to meet these new consumer demands and protect public health.
NES Fircroft has supported the Life Science market for over 20 years, sourcing personnel for engineering, scientific and commercial roles. We recruit highly experienced professionals to the biotechnology, pharmaceutical, diagnostics, and medical devices industries.
We can provide permanent and contract candidates to the Life Science industry across the Quality, Clinical, Regulatory/Compliance, and Engineering disciplines.
If you’re looking for skilled personnel, get in touch with our dedicated Life Science Recruitment teams to find out how we can support you.
Are you looking for a new job? Browse our Life Science vacancies today.